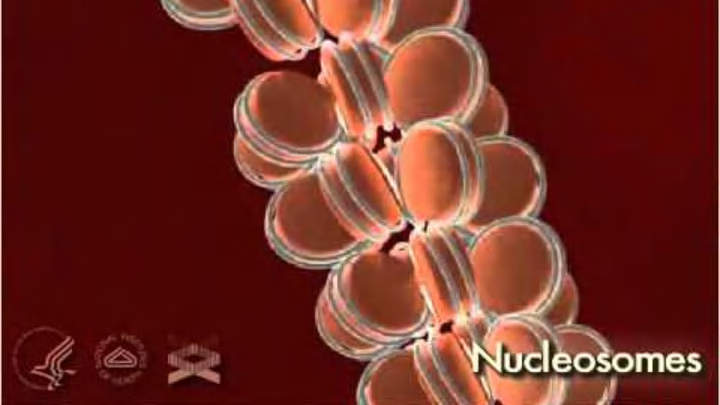
You've heard it tossed around in crime shows, explored in science class, and maybe even shouted by a relative (you'd rather not share this molecule with) at a family reunion: DNA. It's the blueprint of the cell. But what do those three letters actually stand for? Deep breath and... Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
Yes, it does sound like a spell from Harry Potter. But the name isn't a random jumble of words. It's a literal description of what the molecule is made of and where it works. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, DNA is the molecule that carries the instructions needed for living organisms to grow, function, and reproduce. In other words, it's the ultimate biological how-to guide, and every living thing on Earth uses it.
Let's decode.
BREAKING DOWN THE BIG WORD
Deoxyribonucleic Acid looks intimidating, but it's really just three clues stacked together.
Deoxyribo refers to deoxyribose, which is a type of sugar. That sugar forms part of DNA's structural backbone (the twisted ladder). Without this sugar component, the molecule wouldn't have its recognizable shape.
Nucleic tells you where DNA was first found: in the nucleus of cells. It also places DNA in the category of nucleic acids, a group of molecules that includes RNA. These molecules store and transmit genetic information.
And acid? That part reflects DNA's chemical properties. It contains components that give it acidic characteristics. It's less about an acidic taste and more about how the molecule behaves inside the cells.
Put it all together, and Deoxyribonucleic Acid means a sugar-based, nucleus-associated molecule with acidic properties. Suddenly, it's less of a tongue twister and more of a carefully labeled master plan.
WHAT IT DOES AND WHY IT MATTERS
Of course, DNA isn't famous just because of its name. It claims the headlines because it stores the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, hence the blueprint.
DNA is made up of smaller units that link together in a specific order. The sequence of these units is what carries the information. Change the order, and you change the message.
Structurally, DNA forms what's known as a "double helix," the well-known twisted ladder shape. This design isn't just easy to spot in a science textbook; it allows the molecule to be copied efficiently. When cells divide, they need to replicate their DNA so each new cell gets a complete set of instructions. It's the double-stranded structure that enables DNA to be accurately copied when a cell divides.
Another fascinating detail about the molecule is that, as humans, we share 99.9 percent of our DNA. That tiny fraction of difference accounts for individual traits, like eye color, hair color, and nose size. So, while DNA connects us, it also makes us unique.
LIFE'S CODE
Should the term "DNA” ever come up in conversation, you'll know that it stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, a sugar-based, acidic molecule found in the nucleus with a starring role in the creation of life. It might be difficult to pronounce, but its job is very simple: store the instructions that make living things work.
One tiny molecule. Infinite potential for life.