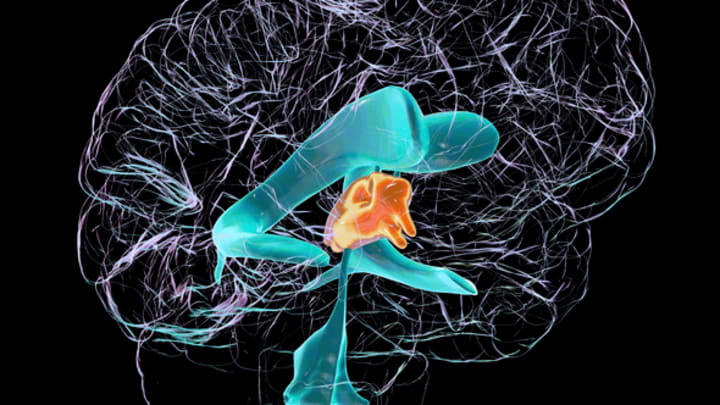
René Descartes once described the pineal gland as “the principal seat of the soul.” Medical knowledge has vastly progressed since his time, though. Here’s what we know about this critical organ.
- Ancient physicians knew the pineal gland was important.
- The gland’s shape influenced its name.
- It’s part of your endocrine system.
- It connects the endocrine and nervous systems.
- The pineal gland was once considered mysterious.
- Descartes was wrong about the gland’s relationship to the mind and soul ...
- ... and tiny animal spirits in your brain.
- It has been called the “third eye.”
- The pineal gland produces single, critical hormone.
- Melatonin is also necessary in reproduction.
Ancient physicians knew the pineal gland was important.
Though the pineal gland wasn’t understood until the 20th century, descriptions of its anatomical location are included in the writings of Galen (ca. 130-ca. 210 CE), a Greek doctor and philosopher.
The gland’s shape influenced its name.
This little gland, located deep in the center of the brain, gets its name from the French pinéal, or “like a pine cone,” itself derived from the Latin pinea, “pine cone.” However, at about one-third of an inch long in adults, the pineal gland is smaller than your average pinecone.
It’s part of your endocrine system.
Though located in your brain, the pineal gland is actually a crucial part of your endocrine system, which regulates major bodily processes such as growth, metabolism, and sexual development through the release and control of hormones.
It connects the endocrine and nervous systems.
The gland translates nerve signals from the sympathetic nervous system into hormone signals.
The pineal gland was once considered mysterious.
Because the pineal gland was the last of the body’s endocrine structures to be discovered, scientists considered it mysterious. Today, we know that unlike much of the rest of the brain, the pineal gland is not isolated from the body by the blood-brain barrier system.
Descartes was wrong about the gland’s relationship to the mind and soul ...

The 16th-century French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes was fascinated with the pineal gland, considering it “the place in which all our thoughts are formed.” Scientists now credit that function to the neocortex.
... and tiny animal spirits in your brain.
Descartes thought that within the pineal gland, tiny animal spirits were like “a very fine wind, or rather a very lively and pure flame,” feeding life into the many small arteries that surround the gland. This was likely due to his pre-modern understanding of anatomy and physiology.
It has been called the “third eye.”
The pineal gland was commonly dubbed the “third eye” for many reasons, including its location in the center of the brain and its connection to light. Mystic and esoteric spiritual traditions suggest it serves as a metaphysical connection between the physical and spiritual worlds.
The pineal gland produces single, critical hormone.
The functions of the pineal gland include synthesizing the hormone melatonin from the neurotransmitter serotonin. Melatonin production determines your sleep-wake cycles and is purely determined by the detection of light and dark. The retina sends these signals to a brain region known as the hypothalamus, which passes them on to the pineal gland. The more light your brain detects, the less melatonin it produces, and vice versa. Melatonin levels are highest at night to help us sleep.
Melatonin is also necessary in reproduction.
Melatonin inhibits the release of reproductive hormones, called gonadotropins, from the pituitary gland, affecting male and female reproductive organs. In this way, melatonin—and therefore the pineal gland—helps regulate sexual development.
Read More Amazing Facts About the Human Body:
A version of this story was published in 2016; it has been updated for 2024.